The Bredesen Protocol - Holistic Approach to Reducing Alzheimer's Progression
Alzheimer's disease, a progressive neuro-degenerative condition, poses significant challenges to both patients and their family carers. As the search for effective treatments continues, the Bredesen Protocol has emerged as a multifaceted approach showing promise in addressing Alzheimer's disease.
Developed by Dr. Dale Bredesen, this protocol emphasises a personalised, holistic strategy aimed at addressing various underlying factors contributing to the disease's progression.
Like to Know More?This page provides an outline of the Bredesen Protocol and the promises that this approach may hold.

Understanding Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder characterised by a decline in cognitive function, memory loss, and behavioral changes. It is the most common cause of dementia, impacting many Australians.
As the disease advances, individuals may struggle with daily tasks, experience difficulties in communication, and undergo personality alterations. Alzheimer's disrupts the brain's ability to transmit signals and maintain connections among neurons, leading to a gradual but severe deterioration in cognitive abilities.
Amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles play pivotal roles in the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Amyloid plaques are formed by the accumulation of beta-amyloid proteins, which cluster together and disrupt neural signaling, causing inflammation and neuronal damage. Tau protein tangles, on the other hand, are abnormal clumps of tau protein that destabilise the internal structure of neurons, hindering their ability to transport essential nutrients and molecules. Both amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles contribute to the degeneration of brain cells, leading to the characteristic cognitive decline seen in Alzheimer's patients.
Conventional treatments for Alzheimer's primarily focus on managing symptoms rather than halting or reversing the disease progression. Medications aim to temporarily improve cognitive function or manage behavioral symptoms but do not address the underlying causes comprehensively. Challenges in conventional approaches include late-stage interventions, limited effectiveness, and potential side effects. The need for alternative strategies is paramount to tackle Alzheimer's more effectively, emphasising prevention, early detection, and interventions that target the fundamental mechanisms of the disease.
Innovative approaches like the Bredesen protocol, which incorporates lifestyle modifications, diet, exercise, and personalised therapeutic interventions, are gaining attention as potential avenues to address Alzheimer's progression comprehensively. These alternative strategies aim to modify multiple risk factors simultaneously and may offer promising paths for managing or even reversing cognitive decline in Alzheimer's patients.
The Genesis of the Bredesen Protocol
Dr. Dale Bredesen is a renowned neuroscientist and physician recognised for his groundbreaking work in neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer's disease. He holds a diverse academic background, having earned degrees in chemistry, medicine, and neuroscience.

Dr. Bredesen served as the Founding President and CEO of the Buck Institute for Research on Ageing (USA), where he conducted extensive research on the molecular mechanisms underlying neurodegeneration. His expertise spans over three decades, during which he has published numerous scientific papers and authored the best-selling book "The End of Alzheimer's," which details his innovative approach to addressing Alzheimer's disease through the Bredesen protocol.
The development of the Bredesen protocol stems from Dr. Bredesen's comprehensive research insights and clinical experiences in treating patients with cognitive decline. His approach integrates findings from diverse scientific disciplines, emphasising the multifactorial nature of Alzheimer's disease.
Through his research, Dr. Bredesen identified various contributing factors to cognitive decline, including inflammation, nutrient deficiencies, insulin resistance, toxic exposures, and more. Drawing from this knowledge, the protocol was formulated as a personalised, multi-modal approach addressing these diverse factors. It encompasses lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, targeted supplementation, cognitive exercises, stress reduction techniques, and personalised interventions aimed at addressing specific imbalances identified through comprehensive testing.
The shift towards personalised treatment in the realm of neurodegenerative diseases marks a departure from the traditional one-size-fits-all approach.
Dr. Bredesen's protocol highlights the importance of recognising individual variations in the underlying causes and mechanisms contributing to cognitive decline. By acknowledging that Alzheimer's disease may manifest differently in different individuals due to unique genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors, the protocol tailors interventions based on individualised assessments. This personalised approach aims to identify and address specific imbalances or deficiencies in each patient, moving away from a generalised treatment strategy that often overlooks individual variations. The emphasis on personalised treatment signifies a shift in the paradigm of Alzheimer's care, offering hope for more effective interventions that consider the intricate and varied nature of the disease among different individuals.
Principles Underlying the Bredesen Protocol
The Bredesen Protocol operates on a foundational framework rooted in the understanding that Alzheimer's disease stems from multifactorial causes and requires a comprehensive, personalised approach for effective intervention.
Its principles centre around the concept of addressing numerous imbalances that contribute to cognitive decline, rather than focusing on a singular target. By identifying and targeting various factors such as inflammation, nutrient deficiencies, insulin resistance, toxins, and other potential contributors, the protocol aims to create an environment conducive to brain health and neuronal resilience. Emphasising the significance of lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, exercise, stress reduction, adequate sleep, and cognitive stimulation, the protocol seeks to optimise brain function and support neuroplasticity.
Additionally, the protocol's personalised nature, tailored to each individual's unique genetic makeup, biomarkers, and health profile, underscores the importance of targeted interventions specific to the identified imbalances through comprehensive testing.
Overall, the Bredesen Protocol embodies a holistic and personalised approach that addresses the complexity of Alzheimer's disease by targeting multiple pathways, aiming to improve brain health and potentially reverse cognitive decline.
Key Components of the Bredesen Protocol
The Bredesen Protocol encompasses a multi-faceted approach comprising several key components tailored to address diverse factors contributing to cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease.
The Bredesen Protocol integrates:
- lifestyle modifications
- dietary changes
- targeted supplementation
- cognitive exercises
- stress management techniques
- and personalised interventions based on individualised assessments
The protocol emphasises a diet rich in brain-supportive nutrients, advocating for a reduction in processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and sugars while promoting a Mediterranean-style diet abundant in vegetables, fruits, healthy fats, and lean proteins. Physical exercise, especially aerobic activities, is encouraged for its positive impact on brain health.
Moreover, the protocol emphasises stress reduction through practices like meditation, adequate sleep, and social engagement to mitigate the detrimental effects of chronic stress on cognition.
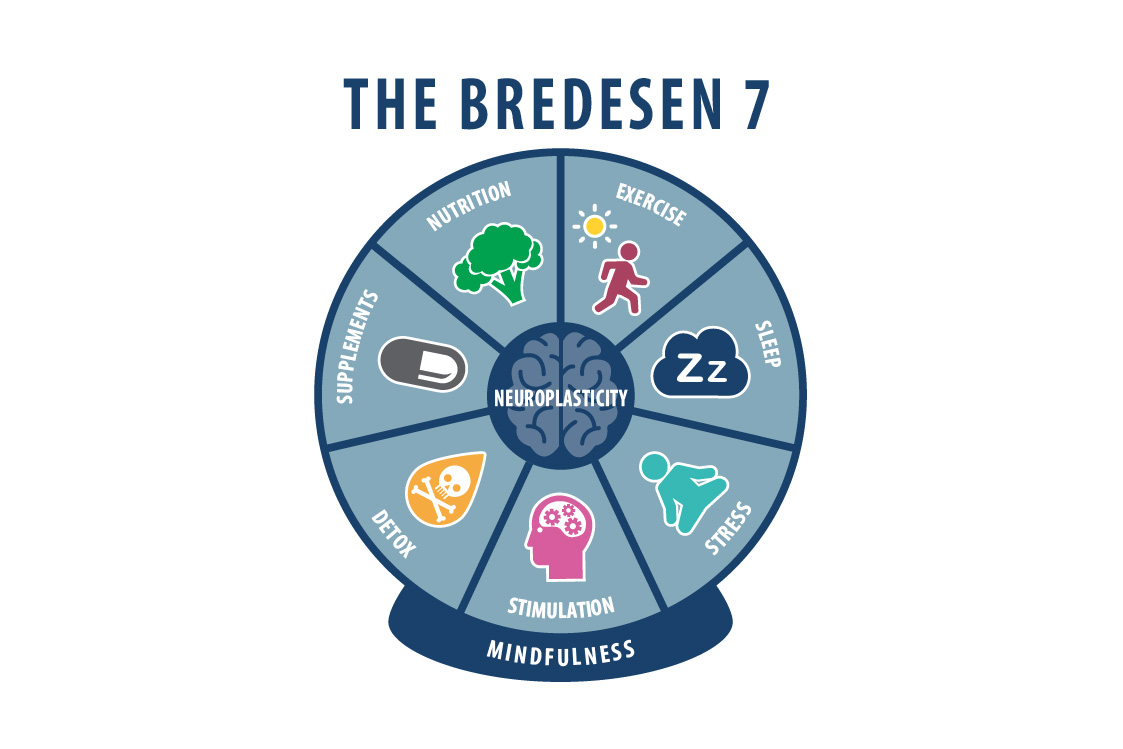
Additionally, the protocol involves targeted supplementation to address specific nutrient deficiencies identified through comprehensive testing. Cognitive stimulation, including brain training exercises and mental challenges, forms another vital aspect to support neuroplasticity and cognitive function.
Overall, the diverse components of the Bredesen Protocol aim to create a holistic and personalised approach to optimise brain health, mitigate risk factors, and potentially reverse cognitive decline in individuals affected by Alzheimer's disease.
Challenges and Criticisms
The Bredesen Protocol, a comprehensive and personalised approach to treating Alzheimer's disease, encounters valid criticisms and limitations.
One key concern revolves around the lack of extensive large-scale clinical trials and long-term data necessary for definitive evidence of its efficacy. While initial studies and anecdotal evidence suggest promise in addressing cognitive decline, the absence of rigorous, randomised controlled trials with larger participant pools over extended periods challenges the ability to substantiate its effectiveness universally.
This dearth of robust data limits the ability to conclusively validate the protocol's impact across diverse populations and various stages of Alzheimer's, casting uncertainty on its broader applicability and standardised use in clinical settings.
A critical limitation affecting the Bredesen Protocol is the insufficient availability of large-scale clinical trials and long-term data. Despite promising outcomes in smaller studies and anecdotal reports, the absence of comprehensive, randomised controlled trials with extensive follow-up periods undermines the ability to establish conclusive evidence supporting the protocol's efficacy.
This gap in robust empirical data hinders a broader validation of the protocol's effectiveness across diverse populations and various stages of Alzheimer's disease. Without substantial evidence from long-term studies, questions persist regarding its reproducibility, generalisability, and standardised applicability as a widely accepted treatment approach.
Accessibility and affordability concerns pose significant challenges in implementing certain aspects of the Bredesen Protocol. Elements such as specialised testing, personalised interventions, and recommended supplements or therapies might present barriers to accessibility for a wider demographic. Availability of these components may vary, and some aspects might not be covered by insurance, limiting access for individuals facing financial constraints or residing in regions with limited healthcare resources. The disparities in accessibility raise questions about equitable distribution and utilisation of the protocol, potentially excluding those who could benefit but lack the means to access its components.
Addressing these concerns by making the protocol more affordable and universally accessible, or exploring alternative approaches aligned with its principles yet more widely available, remains crucial for broadening its potential impact on Alzheimer's care.
Integrating the Bredesen Protocol into Clinical Practice
Healthcare providers are increasingly integrating the Bredesen Protocol into their practices, recognising its potential in addressing the complexities of Alzheimer's disease.
Some clinicians, particularly those specialising in functional or integrative medicine, have embraced this personalised approach to Alzheimer's care. These providers often conduct comprehensive assessments, including detailed patient histories, cognitive evaluations, and laboratory tests, to identify specific imbalances and develop personalised treatment plans aligned with the protocol's principles. While adoption varies, many healthcare providers who incorporate the Bredesen Protocol emphasise lifestyle modifications, nutritional interventions, cognitive exercises, and targeted supplementation as key components in their treatment approach.
Collaboration with other specialists, such as nutritionists, cognitive therapists, and health coaches, might also occur to offer a more comprehensive and holistic care strategy for patients seeking alternative approaches to managing cognitive decline.
Training and education for healthcare professionals interested in implementing the Bredesen Protocol have become increasingly available to support its integration into clinical practice. Various organisations and institutions offer workshops, seminars, and certification programs designed to educate healthcare providers on the protocol's principles, assessment methods, and intervention strategies. These educational initiatives typically cover topics such as understanding the multifactorial nature of Alzheimer's disease, interpreting laboratory tests for identifying imbalances, designing personalised treatment plans, and monitoring patient progress.
Additionally, online resources, peer-reviewed literature, and mentorship opportunities are accessible avenues for healthcare professionals seeking to deepen their knowledge and expertise in applying the Bredesen Protocol. As interest in alternative and personalised approaches to Alzheimer's care continues to grow, the availability of structured training programs and educational resources plays a pivotal role in equipping healthcare providers with the necessary tools and knowledge to implement this protocol effectively within their clinical settings.
Future Directions and Research
Numerous ongoing studies and research initiatives are dedicated to further validating and refining the Bredesen Protocol.
These studies often focus on conducting larger-scale clinical trials with more extensive participant cohorts across diverse demographics and Alzheimer's disease stages. These trials aim to assess the protocol's efficacy, safety, and long-term outcomes rigorously. Additionally, research efforts concentrate on identifying biomarkers and developing standardised assessment tools to better predict and monitor cognitive decline, thus aiding in personalised intervention strategies aligned with the protocol.
Studies exploring the underlying mechanisms targeted by the protocol, such as neuroinflammation, insulin resistance, and synaptic health, contribute to a deeper understanding of how these factors influence Alzheimer's progression and potential treatment responses. Overall, ongoing research endeavors strive to provide robust empirical evidence to support and refine the Bredesen Protocol's application in clinical practice.
Emerging scientific insights continually shape potential advancements and modifications to the Bredesen Protocol.
Advancements in neuroimaging techniques, genetics, and biomarker identification have the potential to enhance the protocol's precision and individualisation. Incorporating cutting-edge technologies for early detection of Alzheimer's-related changes in the brain and identifying genetic risk factors might lead to more targeted and preemptive interventions.
Furthermore, advancements in personalised medicine, such as the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, could assist in analysing multifaceted data sets from patients to tailor interventions more accurately based on individual characteristics. Additionally, ongoing research exploring novel therapeutic targets, innovative lifestyle interventions, and synergistic combinations of treatments could lead to refinements and expansions of the protocol.
As scientific knowledge evolves, incorporating these emerging insights into the Bredesen Protocol may pave the way for more effective and personalised approaches to addressing Alzheimer's disease.
Bredesen Protocol in Australia
In Australia, researchers and healthcare practitioners are showing increasing interest in the Bredesen Protocol and its application, but the extent of its integration into mainstream medical practices is still evolving.
We continue to collect the most current and detailed information regarding the Bredesen Protocol's status in Australia, by referring to recent medical research, and clinical trials with the protocol's introduction into Australia.
Summary
The Bredesen Protocol may result in a major shift in Alzheimer's prevention, offering a personalised and multifaceted approach that addresses contributing factors.
The study involved an intense 36 point program which targeted lifestyle choices. The program included diet changes, brain stimulation, vitamins and supplements. While each program was personalised according the needs of each individual participant, sample components of the program included:
- A major reduction or total elimination of processed foods, simple carbohydrates and gluten
- An increase in consumption of vegetables, fruits and non-farmed fish
- The use of supplements to a persons diet
- Meditation and yoga for stress reduction
- Exercising for at least 30 minutes a day, up to six days per week
- Sleeping between 7 and 8 hours each night
- Fasting for at least 12 hours between dinner and breakfast
While further research and clinical validation are required, the holistic nature of the Bredesen Protocol holds promise in potentially transforming the approach and management of this debilitating condition.